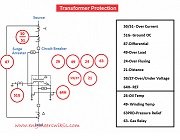
Transformers are critical components in power systems, and their protection is essential to ensure safe and reliable operation. There are several types of transformer protection schemes implemented to detect and mitigate various faults and abnormal conditions. Here are some common types of transformer protection:
- Overcurrent Protection: Overcurrent protection is one of the primary forms of transformer protection. It involves monitoring the current flowing through the transformer windings and tripping the circuit breaker or disconnecting the transformer if the current exceeds a predefined threshold. Overcurrent protection can be implemented using various techniques, including fuses, thermal relays, or electronic overcurrent relays.
- Differential Protection: Differential protection is based on the principle of comparing the currents entering and leaving the transformer. It works by continuously monitoring the current imbalance between the primary and secondary sides of the transformer. If a fault occurs within the protected zone (between the current transformers), the differential current exceeds a set threshold, triggering an alarm or initiating a trip signal to isolate the transformer.
- Buchholz Relay Protection: Buchholz relay is a gas and oil-operated relay installed in the transformer’s oil-filled conservator tank. It provides protection against internal faults, such as short circuits between windings or incipient winding faults. The relay detects the accumulation of gas or oil surge in the conservator tank, caused by the fault, and initiates a trip signal to disconnect the transformer.
- Overvoltage Protection: Overvoltage protection safeguards the transformer against excessive voltage levels that can occur due to system faults or switching operations. It typically involves the use of surge arresters or voltage relays to divert or limit the voltage surge, protecting the insulation of the transformer.
- Overtemperature Protection: Overtemperature protection is crucial for preventing thermal damage to transformers. It employs various techniques to monitor the temperature of transformer components, such as windings, oil, and cooling systems. Temperature sensors, thermocouples, or winding temperature indicators are used to measure temperatures and activate alarms or trips if the temperature exceeds safe limits.
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection: Restricted earth fault protection is used to detect earth faults within the transformer windings. It involves measuring the current flowing through the transformer’s neutral or star-point connection and comparing it with a predefined threshold. If the fault current exceeds the threshold, indicating an earth fault, protective actions such as alarm or trip signals are initiated.
- Over fluxing Protection: Over fluxing or overexcitation protection protects the transformer from excessive magnetic flux levels that can lead to core saturation and increased core losses. It employs devices such as over flux relays or voltage relays to monitor and control the voltage applied to the transformer, ensuring it remains within acceptable limits.
