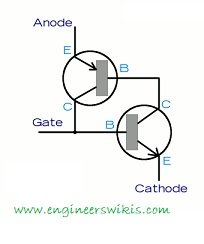
Thyristors are a type of semiconductor device that belongs to the family of four-layer, three-junction devices. They are widely used in power control and switching applications due to their ability to handle high current and voltage levels. Thyristors are also known as silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) and are capable of latching in the conducting state until a specific trigger is applied. Here are some common types of thyristors:
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR): The SCR is the most common type of thyristor. It is a three-terminal device consisting of an anode, a cathode, and a gate. The SCR conducts current when a positive voltage is applied between the anode and cathode and a pulse is applied to the gate. Once triggered, the SCR remains conducting even if the gate current is removed until the forward current drops below a certain threshold. SCRs are widely used in AC power control, motor control, lighting control circuits, and high-power rectification.
- Gate Turn-Off Thyristor (GTO): GTO thyristors are designed with an additional terminal called the gate turn-off terminal. This terminal allows the device to be turned off by applying a negative pulse to the gate. GTO thyristors have fast turn-off characteristics and can be used in applications that require both AC and DC power control, such as in industrial motor drives, traction systems, and reactive power compensation.
- Triac: The triac is a bidirectional thyristor that can conduct current in both directions. It has three terminals: MT1 (main terminal 1), MT2 (main terminal 2), and gate. Triacs are primarily used for AC power control applications, such as in dimmers, motor speed control, and heating control circuits.
- Diac: Although not strictly a thyristor, the diac is often used in conjunction with thyristors for triggering purposes. It is a two-terminal device that exhibits negative resistance characteristics. The diac is commonly used to provide triggering pulses to trigger SCRs or triacs in AC power control circuits.
Thyristors are known for their high current and voltage handling capabilities, making them suitable for applications where power control and switching are required. They are commonly used in industrial systems, electric motor drives, power supplies, lighting control, and heating control circuits.
It’s important to note that thyristors require proper gate triggering techniques and protection circuitry to ensure safe and reliable operation. Additionally, thermal management is crucial due to the high power dissipation associated with thyristors.
