Rotary encoders are electromechanical devices used to measure the angular position, speed, and direction of rotation of a shaft or object. They convert mechanical rotation into electrical signals that can be processed by electronic systems. Rotary encoders are widely used in various applications that require precise position or speed feedback. Here are some key points about rotary encoders:
Types of Rotary Encoders:
- Incremental Rotary Encoders: Incremental encoders generate electrical pulses as the shaft rotates. They provide information about the relative position and speed of rotation. The output typically consists of two channels, A and B, which produce pulse trains with a phase difference (quadrature output). By counting the pulses and monitoring the phase relationship, the position and rotation direction can be determined. Incremental encoders do not provide absolute position information and require a reference point (known as a home or index pulse) for initialization.
- Absolute Rotary Encoders: Absolute encoders provide direct position information without the need for referencing. They have multiple tracks or coding schemes that represent the absolute position of the shaft. Each track provides a unique digital code corresponding to a particular position. Absolute encoders can provide high-resolution position feedback and are often used in applications where accurate position control is critical.
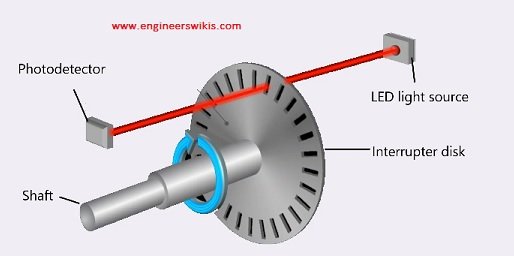
- Optical Rotary Encoders: Optical encoders use a light source, typically an LED, and a photoelectric sensor to detect markings or patterns on a rotating disc. The disc may have reflective or transmissive markings, and as the disc rotates, the changes in the light pattern are detected to determine the position or speed.
- Magnetic Rotary Encoders: Magnetic encoders use magnets and Hall effect sensors to measure the rotation of a magnetic disc or magnetic poles on a rotating shaft. The magnetic field changes detected by the sensors provide position and speed information.
Applications of Rotary Encoders:
- Robotics and Automation: Rotary encoders are extensively used in robotics and automation systems to provide precise position feedback for robotic arms, CNC machines, and automated assembly lines. They enable accurate control of motion, positioning, and path planning.
- Industrial Machinery: Rotary encoders are employed in various industrial machinery, including machine tools, printing presses, packaging machines, and conveyor systems. They provide feedback for controlling speed, position, and synchronization of moving parts.
- Motion Control Systems: Rotary encoders are crucial components in motion control systems, such as servo motors and stepper motors. They provide feedback for closed-loop control, ensuring accurate and precise motion control.
- Automotive: Rotary encoders are used in automotive applications, such as throttle position sensing, steering angle measurement, and ABS systems. They provide real-time data for vehicle control, stability, and safety.
- Robotics and Drones: Rotary encoders are essential in robotic systems and drones for position feedback, motor control, and navigation.
- Medical Devices: Rotary encoders find applications in medical devices, such as surgical robots, imaging equipment, and patient positioning systems, where precise motion control and positioning are critical.
- Consumer Electronics: Rotary encoders are used in various consumer electronics devices, including audio equipment, cameras, gaming consoles, and home appliances, for volume control, menu navigation, and user interaction.
Rotary encoders are versatile devices that provide accurate position and speed feedback in a wide range of applications. They enable precise control, improve efficiency, and contribute to the overall performance and functionality of electromechanical systems.
