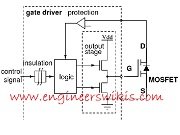
A gate driver for MOSFETs is a specialized integrated circuit (IC) or module designed to provide the necessary voltage and current signals to efficiently control the switching of MOSFETs. The gate driver ensures that the MOSFET transitions between its on and off states rapidly and reliably, minimizing power losses and optimizing performance. Here are some key features and functions of a typical MOSFET gate driver:
Voltage Level Shifting: MOSFETs require a gate-source voltage (VGS) above a certain threshold to turn on fully. The gate driver incorporates voltage level shifting circuitry to generate a higher voltage than the control signal provided by the microcontroller or control circuit. This voltage level shifting ensures that the MOSFET turns on and off as required.
Gate Drive Voltage: MOSFETs generally have a gate-source capacitance (CGS) that needs to be charged or discharged quickly for efficient switching. The gate driver provides a high-current drive capability to charge or discharge the gate capacitance rapidly, reducing switching times and minimizing power losses.
Protection and Fault Detection: Gate drivers often include protection features to enhance the reliability and robustness of the MOSFETs. These features can include overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, undervoltage lockout, and thermal shutdown. Fault detection circuits monitor the MOSFET operation and provide feedback to the control system in case of any abnormal conditions.
Dead-Time Control: When using MOSFETs in a half-bridge or full-bridge configuration, it is crucial to avoid simultaneous conduction of the high-side and low-side MOSFETs, which can lead to shoot-through current and potentially damage the devices. The gate driver incorporates dead-time control to introduce a delay between the turn-off of one MOSFET and the turn-on of the complementary MOSFET, ensuring proper commutation.
Isolation: In some applications, such as motor drives or power converters, galvanic isolation between the control circuitry and the high-voltage MOSFETs is necessary for safety reasons. Isolated gate drivers use techniques like optocouplers or transformers to provide electrical isolation, protecting the control circuitry from high voltage transients.
Driver Configuration: Gate drivers can be available as single-channel or multi-channel configurations, depending on the number of MOSFETs to be driven. Multi-channel gate drivers enable simultaneous control of multiple MOSFETs, which is useful in high-power applications where multiple devices are used in parallel.
Gate drivers for MOSFETs come in various forms, including discrete ICs, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), and modules. The selection of a gate driver depends on the specific requirements of the MOSFETs being used, such as voltage and current ratings, switching speed, and protection features needed for the application.
