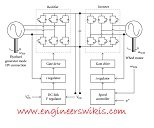
AC-DC-AC power conversion, also known as AC-to-DC-to-AC power conversion or AC/DC/AC conversion, refers to the process of converting alternating current (AC) power into direct current (DC) power, and then converting it back into AC power. This conversion is commonly used in various applications, including power electronics, renewable energy systems, motor drives, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Here’s a general overview of the AC-DC-AC power conversion process:
- AC-to-DC Conversion (Rectification): The first step is to convert the incoming AC power into DC power. This is achieved using a rectifier circuit, which typically consists of diodes or thyristors (SCRs). The rectifier circuit allows current to flow in only one direction, resulting in a pulsating DC waveform. Depending on the application, different rectifier configurations can be used, such as half-wave rectification, full-wave rectification, or bridge rectification.
- DC-to-AC Conversion (Inversion): Once the AC power is converted into DC power, it can be further processed to generate a new AC waveform. This is accomplished using an inverter circuit. The inverter circuit takes the DC input and produces an AC output waveform that can have various characteristics, such as frequency, voltage, and waveform shape. Inverters can be designed using various switching devices, such as transistors (IGBTs or MOSFETs), thyristors, or gate turn-off thyristors (GTOs), to control the flow of current and voltage.
- Filtering and Control: In AC-DC-AC power conversion, additional components are often included to filter out harmonics, smooth the waveform, and provide control and protection features. These components may include capacitors, inductors, filters, voltage regulators, and control circuits. The control circuitry ensures proper synchronization, voltage regulation, and protection against overvoltage, undervoltage, and short circuits.
Applications of AC-DC-AC Power Conversion:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): AC-DC-AC conversion is widely used in motor drives and VFDs. The AC power is converted to DC to control the speed and torque of AC motors, and then converted back to AC at the desired frequency and voltage. This allows precise control of motor speed and energy-efficient operation.
- Renewable Energy Systems: AC-DC-AC conversion is essential in renewable energy systems, such as solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind power systems. The AC power generated from the renewable energy sources is first rectified to DC power, which is then inverted back to AC power to match the grid frequency and voltage.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): UPS systems utilize AC-DC-AC conversion to provide backup power during utility power outages. The incoming AC power is rectified to DC power, which charges the battery bank. When a power outage occurs, the stored DC power is inverted back to AC power to supply the connected loads.
- Grid Interconnection and Power Quality: AC-DC-AC conversion is employed in grid interconnection applications, such as distributed generation systems and energy storage systems. It allows power generated from renewable sources or stored in batteries to be synchronized and injected into the utility grid while maintaining power quality and meeting grid regulations.
- Industrial Power Systems: AC-DC-AC conversion is used in various industrial applications where precise control of AC power is required. This includes applications such as industrial motor drives, uninterruptible power supplies for critical equipment, and power quality improvement systems.
AC-DC-AC power conversion plays a critical role in various power electronic systems, enabling efficient power transfer, control, and integration of different power sources. The specific design and configuration of the conversion process depend on the application requirements, load characteristics, and system constraints.
