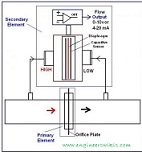
A differential pressure transmitter is a type of pressure sensor used to measure the difference in pressure between two points in a system. It is specifically designed to measure the pressure drop across a device, such as a filter, valve, or flow meter.
The basic operation of a differential pressure transmitter involves comparing the pressure at two different points and generating an output signal proportional to the pressure difference. It typically consists of two pressure sensing elements, often referred to as the high-side and low-side ports.
Here’s how a differential pressure transmitter works:
- High-Side and Low-Side Pressure Measurement: The high-side port of the transmitter is connected to the higher pressure point, while the low-side port is connected to the lower pressure point. The pressure difference between these two points is the parameter of interest.
- Sensing Elements: The differential pressure transmitter contains two pressure sensing elements, one for each port. These sensing elements can be based on various technologies such as strain gauges, capacitive sensors, or piezoresistive sensors. The sensing elements convert the pressure difference into an electrical signal.
- Signal Processing: The electrical signal generated by the sensing elements is processed by the transmitter’s electronics. This includes amplification, filtering, linearization, and temperature compensation to provide an accurate and stable output signal.
- Output Signal: The output signal of a differential pressure transmitter is typically a standardized electrical signal, such as a 4-20 mA current loop or a 0-10 V voltage signal. The output is proportional to the differential pressure being measured, allowing for easy integration with control systems or data acquisition devices.
Differential pressure transmitters have various applications across industries, including:
- HVAC systems: Monitoring air flow and filter conditions.
- Process control: Measuring pressure drops across valves, filters, or heat exchangers.
- Flow measurement: Calculating flow rates based on the pressure difference across an orifice plate or flow meter.
- Liquid level measurement: Determining the level in tanks or vessels by analyzing the pressure difference caused by liquid height.
The advantages of using a differential pressure transmitter include high accuracy, wide pressure range capabilities, and compatibility with different media. Additionally, they can be configured for various installation orientations and are available in different sizes and form factors to suit specific application requirements.
What are the types of pressure sensing elements used in differential pressure transmitters?
Several types of pressure sensing elements are used in differential pressure transmitters. The choice of sensing element depends on factors such as the application requirements, pressure range, accuracy, and environmental conditions. Here are some common types:
- Strain Gauges: Strain gauges are widely used in differential pressure transmitters. They consist of thin metal foils or semiconductor strips that deform under pressure, causing a change in electrical resistance. The strain gauges are bonded to a diaphragm, and the resistance change is measured to determine the differential pressure.
- Capacitive Sensors: Capacitive sensors utilize changes in capacitance to measure pressure. They consist of two parallel plates separated by a dielectric material. The pressure causes deflection of a diaphragm, changing the distance between the plates and thereby altering the capacitance. The change in capacitance is measured to determine the differential pressure.
- Piezoresistive Sensors: Piezoresistive sensors use the principle of piezoresistance, where the electrical resistance of certain materials changes under mechanical stress. These sensors typically consist of a diaphragm with piezoresistive elements bonded to it. The pressure causes deformation of the diaphragm, resulting in a change in resistance. The resistance change is measured to calculate the differential pressure.
- Variable Capacitance Sensors: Variable capacitance sensors operate based on changes in the distance between two plates due to pressure variations. They use a diaphragm that moves in response to pressure, altering the distance between the plates and thus changing the capacitance. The capacitance change is measured to determine the differential pressure.
- Thermal Sensors: Thermal sensors, such as thermal anemometers or thermal mass flow sensors, can also be used in certain differential pressure applications. They work by measuring the heat transfer or changes in temperature caused by the fluid flow or pressure difference.
These are some of the commonly used pressure sensing elements in differential pressure transmitters. Each type has its own advantages and limitations, and the selection depends on the specific requirements of the application, including accuracy, stability, pressure range, temperature range, and compatibility with the measured media.
