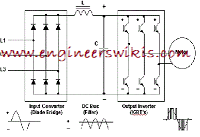
A variable frequency drive (VFD), also known as an adjustable frequency drive or variable speed drive, is an electronic device used to control the speed and torque of an electric motor. It is a common component in various industrial and commercial applications where precise motor control and energy efficiency are desired. Here’s how a variable frequency drive works:
Functionality:
A VFD regulates the speed of an electric motor by controlling the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. It converts the incoming fixed-frequency AC power from the mains into a variable frequency and voltage output that matches the requirements of the motor. By adjusting the frequency and voltage, the VFD can precisely control the motor speed and torque.
Key Components of a VFD:
- Rectifier: The rectifier section of the VFD converts the incoming AC power into DC power. It typically consists of diodes or thyristors that rectify the AC waveform into a pulsating DC waveform.
- DC Bus: The DC bus section of the VFD acts as an energy storage element. It smooths out the pulsating DC waveform and provides a stable DC voltage for the inverter section.
- Inverter: The inverter section of the VFD converts the DC power from the DC bus back into an AC output. It uses power electronic switches, such as insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), to generate a variable frequency and voltage output waveform. The frequency and voltage output can be adjusted based on the motor speed and torque requirements.
- Control Unit: The control unit of the VFD consists of a microprocessor or digital signal processor (DSP) that monitors the motor’s speed, current, and other parameters. It receives input signals from the user interface or external control system and adjusts the VFD’s output based on the desired motor speed and torque.
Advantages of Variable Frequency Drives:
- Energy Efficiency: VFDs enable energy savings by allowing precise control over motor speed. By reducing the motor speed to match the load requirements, energy consumption can be significantly reduced compared to running the motor at full speed continuously.
- Speed and Torque Control: VFDs provide accurate speed and torque control for electric motors, allowing for precise operation in various applications. The motor speed can be adjusted dynamically to match process requirements, resulting in improved control and productivity.
- Soft Start and Stop: VFDs offer soft start and stop capabilities, gradually ramping up or down the motor speed instead of subjecting the motor to sudden voltage and current changes. This feature reduces mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment, extending their lifespan.
- Motor Protection: VFDs incorporate various motor protection features, such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and undervoltage protection. They can monitor motor parameters and respond to abnormal conditions, preventing motor damage and improving overall system reliability.
- Reduced Mechanical Wear: By controlling the motor speed and torque, VFDs can reduce mechanical wear and tear on the motor and connected equipment. This leads to longer equipment life and reduced maintenance costs.
Variable frequency drives are widely used in applications such as HVAC systems, pumps, fans, conveyors, machine tools, and many other motor-driven systems where precise control, energy efficiency, and motor protection are crucial.
